MANO Software Components
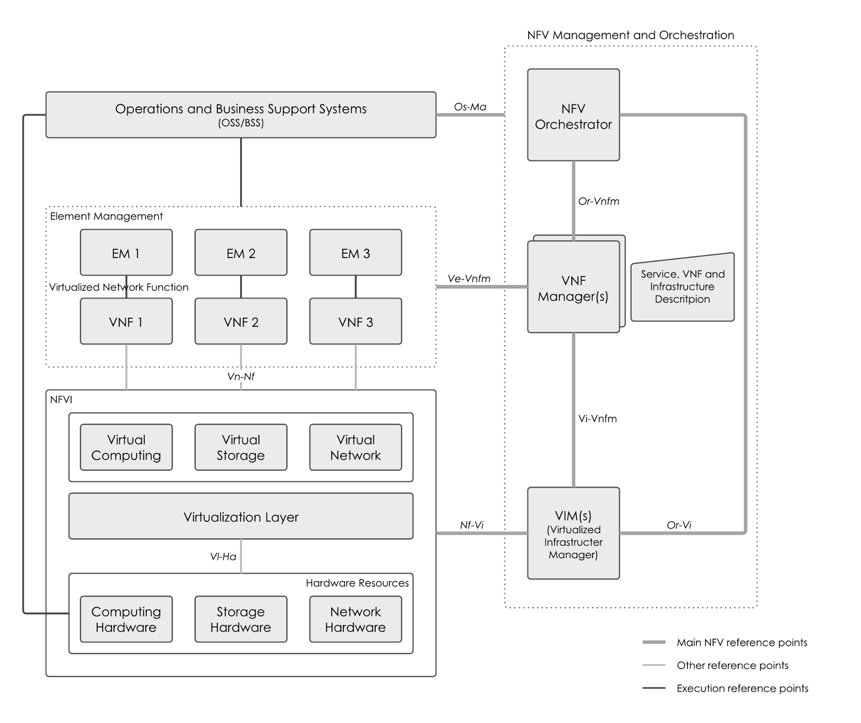
The Virtualized Infrastructure Manager (VIM) is responsible for managing the NFV infrastructure (compute, network and storage resources).
The VIM provides a northbound interface for the VNF Manager and NFV Orchestrator, and abstracts rest of the system from the details of underlying cloud management platform.
Reference: ETSI GS NFV 002 V1.2.1 (2014-12)
VNF Manager
The VNF Manager (VNFM) manages the lifecycle of the components and services. VNFM oversees the management of VNF instances, as well as the following:
-
Starting the VNF from its descriptor and managing the VNF
-
Scaling out/in and up/down of VNFs
-
Monitoring and collecting parameters that determine the health of the VNF
NFV Orchestrator
The NFV Orchestrator (NFVO) is responsible for network service management, such as creating virtual function instances to meet service requirements. The NFVO manages network service lifecycle and resource orchestration across multiple VIMs.
Other NFVO functionality includes the following:
-
Onboarding new network services and virtual network function packages
-
Managing global resources, such as the physical and logical network topology of how various VNFs and PNFs connect
-
Handling policy management related to scalability, reliability, and high availability for network service instances
-
Authorizing network functions virtualization infrastructure (NFVI) resource requests
-
Managing the network service (NS) service templates in the NS catalog
-
Simplifying the job of launching new network services
Interface
Designed with open, standards-based APIs, such as NETCONF and REST, and common information models, such as YANG, the Os-ma-nfvo interface is exposed through open, standards-based interfaces such as REST. This design enables upper-level orchestrators, such as Business Process Orchestrators or Service Orchestrators, to automate the entire service bring-up process.
|
© 2020 RIFT. All Rights Reserved |
Published on 1/26/2021, 4:38 PM |
